Inheritance in java is the most important topic. Inheritance is an important concept/feature of Object-Oriented. The most common question asked in an interview is “What is multiple inheritances in Java” and “Why multiple inheritances is not supported in Java”. Here we will discuss it in detail.
Here is the table content of the article will we will cover this topic.
1. What is multiple inheritance?
2. Why Java doesn’t support multiple inheritances?
3. How to achieve multiple inheritances?
4. What is the diamond problem in java?
5. How to resolve the diamond problem in java 8?
What is multiple inheritance?
As you know a class can extend the features of other classes by use of inheritance. When a class extends more than one class is known as multiple inheritance. But Java doesn’t allow it because it creates the diamond problem and is too complex to manage. We can achieve multiple inheritances by use of an interface. Firstly, we will concentrate on the current discussion.
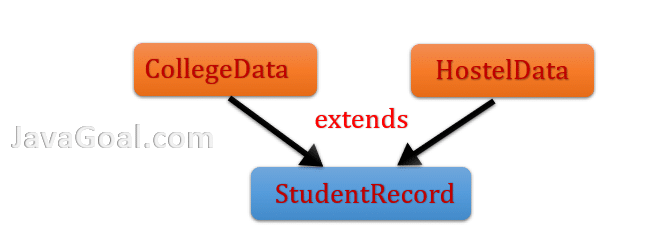
Here CollegeData and HostelData are two classes that are extended by the StudentRecord class. This is known as multiple inheritances. But in java, it is not possible to implement it. We will learn what is the reason behind and why java doesn’t support multiple inheritances.
Why Java doesn’t support multiple inheritances?
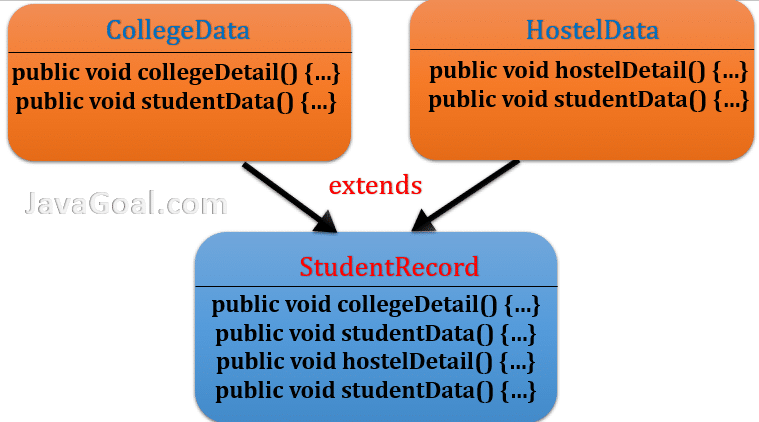
Let’s say we have two classes CollegeData and HostelData. Both classes have student records and have some methods. Here we have two methods in each class and one method is common in both classes.
StudentRecord is another class that extends both classes(CollegeData and HostelData). It means the StudentRecord inherited all the methods of CollegeData and HostelData.
class CollegeData
{
public void collegeDetail()
{
System.out.println("College Name : DCSA");
System.out.println("College Grade : A");
System.out.println("University of College : KUK");
}
public void studentData()
{
System.out.println("courses of Student : MCA, MTECH, MBA, BCA");
}
}
class HostelData
{
public void hostelDetail()
{
System.out.println("Hostel Name : RAMA");
System.out.println("Hostel location : KUK");
}
public void studentData()
{
System.out.println("Student selected on based : Percentage, Financial condition");
}
}
public class StudentRecord extends CollegeData, HostelData
{
public static void main (String[] args)
{
StudentRecord obj = new StudentRecord ();
obj.collegeDetail();
obj.studentData();
obj.hostelDetail();
obj.studentData();
}
}
Output: Compilation error
There may be many reasons to show a compilation error. We will discuss the two major reasons.
First reason: You have seen that CollegeData and HostelData classes are extended by the StudentRecord class. Both classes have a common method studentData() that is inherited by StudentRecord. When the programmer tries to call studentData() method in StudentRecord Class then the compiler will get confused about which method would be called? That’s the main reason why Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance.
Second reason: As must be heard about the constructor chaining. A constructor can call the constructor of the superclass and the constructor defined in the same class. By default, JVM is dealing with the constructor chaining because if you are creating an object by a new keyword then JVM invokes the constructor of that class and that constructor invokes the superclass constructor.
When the programmer tries to create an object of StudentRecord then the compiler will get confused about whose constructor should be invoked?
How to achieve multiple inheritance using interface in java?
We can achieve multiple inheritances by the use of interfaces. As you already know a class can implement any number of interfaces, but it can extend only one class. Before Java 8, Interfaces could have only abstract methods. It just defined the contract implemented by concrete classes.

Here we will discuss it with two examples.
scenario 1: Firstly, we will see if both interfaces don’t contain any common method. It will not create any ambiguity.
scenario 2: After that, if the interface has some common method then how to resolve the ambiguity?
scenario 1: Let’s discuss the first scenario when interfaces haven’t any common method. Here we have two interfaces and one concrete class that implements them and provide the implementation to the abstract method.
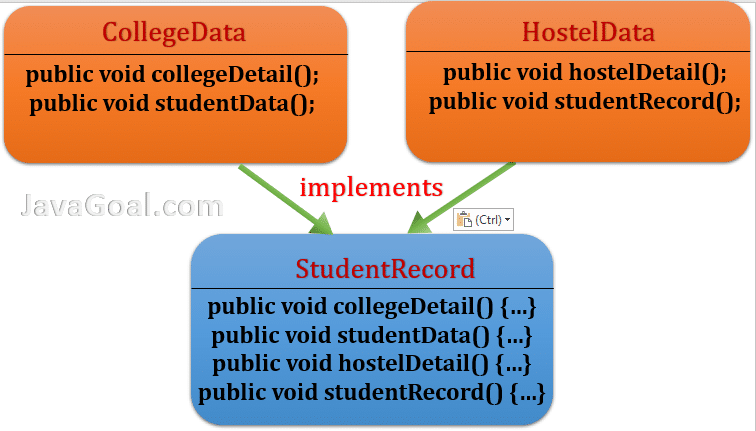
Let’s say we have two interfaces CollegeData and HostelData. Both classes have some methods, but they haven’t any common method. Here we have two methods in each class that is inherited by the concrete class.
StudentRecord is a concrete class that is implementing both interfaces. It means the StudentRecord inherited all the methods and provide the implementation to the method of CollegeData and HostelData interface.
interface CollegeData
{
public void collegeDetail();
public void studentData();
}
interface HostelData
{
public void hostelDetail();
public void studentRecord();
}
public class StudentRecord implements CollegeData, HostelData
{
@Override
public void hostelDetail()
{
System.out.println("Hostel Name : RAMA");
System.out.println("Hostel location : KUK");
}
@Override
public void studentRecord()
{
System.out.println("Student selected on based : Percentage, Financial condition");
}
@Override
public void collegeDetail()
{
System.out.println("College Name : DCSA");
System.out.println("College Grade : A");
System.out.println("University of College : KUK");
}
@Override
public void studentData()
{
System.out.println("courses of Student : MCA, MTECH, MBA, BCA");
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
StudentRecord obj = new StudentRecord();
obj.collegeDetail();
obj.studentData();
obj.hostelDetail();
obj.studentData();
}
}
Output: College Name : DCSA
College Grade : A
University of College : KUK
courses of Student : MCA, MTECH, MBA, BCA
Hostel Name : RAMA
Hostel location : KUK
courses of Student : MCA, MTECH, MBA, BCA
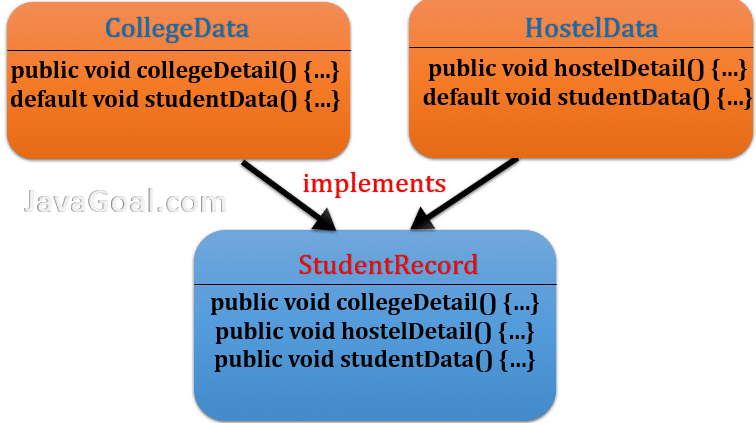
Scenario 2: Let’s discuss the second scenario where we have a common method in both interfaces. When a concrete class will implement both the interfaces and provides the implementation then how the compiler will take a decision? what method should be invoked?
To resolve this problem we will use default methods that were introduced in Java 8. You can read the default method in detail.
interface CollegeData
{
public void collegeDetail();
default void studentData()
{
System.out.println("courses of Student : MCA, MTECH, MBA, BCA");
}
}
interface HostelData
{
public void hostelDetail();
default void studentData()
{
System.out.println("Student selected on based : Percentage, Financial condition");
}
}
public class StudentRecord implements CollegeData, HostelData
{
@Override
public void hostelDetail()
{
System.out.println("Hostel Name : RAMA");
System.out.println("Hostel location : KUK");
}
@Override
public void collegeDetail()
{
System.out.println("College Name : DCSA");
System.out.println("College Grade : A");
System.out.println("University of College : KUK");
}
@Override
public void studentData()
{
CollegeData.super.studentData();
HostelData.super.studentData();
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
StudentRecord obj = new StudentRecord();
obj.collegeDetail();
obj.hostelDetail();
obj.studentData();
}
}
Output: College Name : DCSA
College Grade : A
University of College : KUK
Hostel Name : RAMA
Hostel location : KUK
courses of Student : MCA, MTECH, MBA, BCA
Student selected on based : Percentage, Financial condition
In the above example to resolve the diamond problem, we are using the super keyword and overriding the method again. You can read the diamond problem in detail.
What is the diamond problem in java?
As you know, multiple inheritance doesn’t support java. To achieve multiple inheritance, we can use the default method and static method in java 8. If you haven’t read the article “How to achieve multiple inheritance by inhertface” yet. Then you should read it first, after that, it makes sense to you.
By using of default method in the interface, we can achieve multiple inheritances. But the diamond problem is still there. If interfaces have a common default method, Let’s see how it goes in the problem.

Also, Here we are using multiple inheritances by use of interfaces. The parent interface is University. Two interfaces, CollegeData and HostelData, is extending the university interface. Both interfaces are implemented by a concrete class StudentRecord. Hence, You can see in the image the inheritance is in a diamond shape.
Now try to find out the problem area. The parent interface University has a default method that is extended by another interface. The CollegeData and HostelData interface has a common default method inherited by StudentRecord.
Now, these two method definitions in the StudentRecord have the same signature, which method would the StudentRecord inherit? Which method should be invoked when we try to call studentData() in StudentRecord? Therefore, It is the diamond problem.
interface University
{
default void universityInfo()
{
System.out.println("University Name : KUK");
System.out.println("Number of departments : 100");
System.out.println("Grade of university : A");
}
}
interface CollegeData extends University
{
public void collegeDetail();
default void studentData()
{
System.out.println("courses of Student : MCA, MTECH, MBA, BCA");
}
}
interface HostelData extends University
{
public void hostelDetail();
default void studentData()
{
System.out.println("Student selected on based : Percentage, Financial condition");
}
}
public class StudentRecord implements CollegeData, HostelData
{
@Override
public void hostelDetail()
{
System.out.println("Hostel Name : RAMA");
System.out.println("Hostel location : KUK");
}
@Override
public void collegeDetail()
{
System.out.println("College Name : DCSA");
System.out.println("College Grade : A");
System.out.println("University of College : KUK");
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
StudentRecord obj = new StudentRecord();
obj.universityInfo();
obj.collegeDetail();
obj.hostelDetail();
obj.studentData();
}
}
Output: Compilation error
How to resolve the diamond problem in java 8?
The diamond problem can be resolved manually. In this case, resolve the conflict manually by using the super keyword within the StudentRecord class to explicitly mention which method the definition wants to use. The super keyword uses to call the method of the parent class/interface.
Let’s see how it works. So, here we will override the studentData() method. In which we are calling the method of parent interface by use of the super keyword.
interface University
{
default void universityInfo()
{
System.out.println("University Name : KUK");
System.out.println("Number of departments : 100");
System.out.println("Grade of university : A");
}
}
interface CollegeData extends University
{
public void collegeDetail();
default void studentData()
{
System.out.println("courses of Student : MCA, MTECH, MBA, BCA");
}
}
interface HostelData extends University
{
public void hostelDetail();
default void studentData()
{
System.out.println("Student selected on based : Percentage, Financial condition");
}
}
public class StudentRecord implements CollegeData, HostelData
{
@Override
public void hostelDetail()
{
System.out.println("Hostel Name : RAMA");
System.out.println("Hostel location : KUK");
}
@Override
public void collegeDetail()
{
System.out.println("College Name : DCSA");
System.out.println("College Grade : A");
System.out.println("University of College : KUK");
}
@Override
public void studentData()
{
HostelData.super.studentData();
CollegeData.super.studentData();
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
StudentRecord obj = new StudentRecord();
obj.universityInfo();
obj.collegeDetail();
obj.hostelDetail();
obj.studentData();
}
}
Output: University Name: KUK
Number of departments: 100
Grade of University: A
College Name: DCSA
College Grade: A
University of College: KUK
Hostel Name: RAMA
Hostel location: KUK
Student selected on based: Percentage, Financial condition
courses of Student: MCA, MTECH, MBA, BCA



Hi,
Can you give me an example of this concept?
The multiple inheritances also creates problems in constructor chaining